
Software is a collection of instructions and data that enable computers and other electronic devices to perform specific tasks or functions. It is a crucial component of modern technology, powering everything from operating systems and applications to embedded systems and cloud services…
:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:
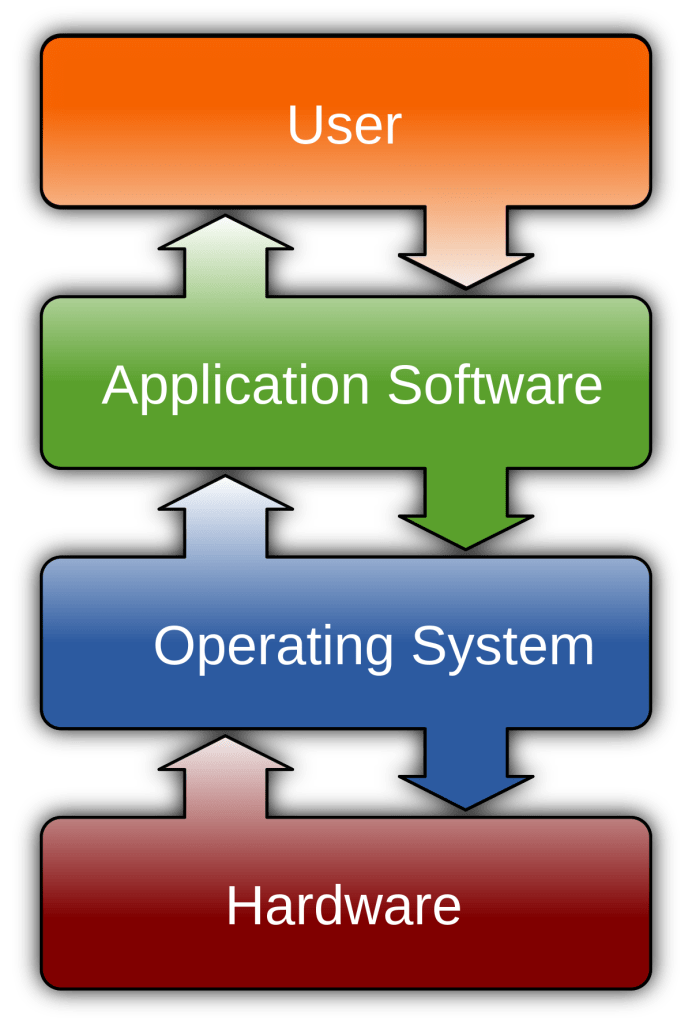
Software can be broadly categorized into two main types: system software and application software. System software includes operating systems, device drivers, and firmware, which manage hardware and provide a platform for other software to run. Application software, on the other hand, serves end-users by providing tools and functionality for tasks such as word processing, gaming, or web browsing…
:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:
Software is typically created through programming or coding, where developers write lines of code using programming languages. These instructions are then compiled or interpreted by a computer’s processor, translating the human-readable code into machine code that the hardware can execute…
:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:
The software industry is dynamic and constantly evolving, with new updates, versions, and applications being developed to meet the changing needs of users. Whether it’s the software on your smartphone, the web browsers you use, or the operating system that powers your computer, software is the invisible force that drives and shapes the digital world we live in today…
:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:-:

Computer software can be classified into various types based on its functionality, purpose, and usage. Here, we’ll explore some of the primary categories of computer software.
1. System Software :-
Operating Systems (OS) : These are the core software that manage hardware resources, provide a user interface, and enable the execution of other software. Popular examples include Microsoft Windows, macOS, and Linux.
• Device Drivers : Device drivers facilitate communication between the hardware devices and the operating system. They allow peripherals like printers, graphics cards, and network adapters to work with the computer.
• Firmware : Firmware is software that is embedded in hardware devices, such as BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) on a motherboard or firmware on your smartphone. It controls the basic functions and initializes hardware during the boot process.
2. Application Software :-
• Word Processing Software : These applications, like Microsoft Word or Google Docs, enable users to create, edit, and format text documents.
• Spreadsheet Software : Programs like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets help users manage data, perform calculations, and create charts and graphs.
• Presentation Software : Tools like Microsoft PowerPoint and Google Slides allow users to create multimedia presentations.
• Database Software : Database management systems, such as MySQL and Microsoft Access, store, organize, and retrieve data efficiently.
• Web Browsers : Applications like Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Safari are used to access and navigate the internet.
• Multimedia Software. : This category includes audio and video editing software (e.g., Adobe Premiere Pro and Audacity), media players (e.g., VLC), and graphic design tools (e.g., Adobe Photoshop).
• Gaming Software : Video games and gaming platforms, such as Steam, PlayStation, and Xbox, are a significant part of the software industry.
• Productivity Software : Tools like project management software (e.g., Trello), note-taking apps (e.g., Evernote), and communication software (e.g., Slack) improve productivity.
• Graphics Software : Graphic design and illustration software, such as Adobe Illustrator and CorelDRAW, are used for creating visual content.
• Educational Software : Educational programs and e-learning platforms like Moodle and Khan Academy aid in teaching and learning.
• Financial Software : Applications like QuickBooks and Quicken help with accounting, budgeting, and financial management.
• Antivirus and Security Software : These programs protect computers from malware, viruses, and other online threats. Examples include Norton, McAfee, and Windows Defender.
• Utility Software : Utility software includes tools like file compression software (e.g., WinZip), disk cleanup, and system optimization programs.
• Communication Software : Email clients (e.g., Microsoft Outlook), instant messaging apps (e.g., WhatsApp), and video conferencing tools (e.g., Zoom) fall into this category.
3. Middleware Software :-
• Middleware : Middleware software acts as an intermediary between different applications, enabling them to communicate and share data. It’s often used in enterprise-level systems to facilitate integration between software components.
4. Programming Software :-
• Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) : IDEs like Visual Studio, Eclipse, and PyCharm provide tools for developers to write, test, and debug code efficiently.
• Text Editors : Text editors like Notepad++, Sublime Text, and Vim are simpler tools for writing and editing code.
• Compilers and Interpreters : These software types translate high-level programming languages into machine code or execute code directly. Examples include GCC (C/C++ compiler) and Python’s interpreter.
5. Embedded Software :-
• Embedded Systems : Software embedded in hardware devices like microwave ovens, cars, or home automation systems to control specific functions.
6. Open Source Software :-
• Open Source : These are software applications with source code that is open to the public for viewing, modification, and distribution. Linux, Apache, and LibreOffice are well-known open-source software.
7. Proprietary Software :-
• Proprietary : Proprietary software is owned by a specific organization or company. It includes commercial software like Microsoft Office and Adobe Creative Suite.
8. Freeware, Shareware, and Trial Software :-
• Freeware : Software that is free to use with no payment required.
• Shareware : Software that is free to use for a trial period but requires payment for continued use.
• Trial Software : Fully-featured software that is free for a limited time or with limited functionality. Users can purchase the full version for extended features.
9. Cloud-Based Software :-
• SaaS (Software as a Service) : Cloud-based software accessible over the internet, such as Google Workspace and Salesforce, which provides various applications on a subscription basis.
10. Mobile Apps :-
• Mobile Operating Systems : iOS and Android power mobile devices, while mobile apps, available through app stores, cover a wide range of categories, from social media to gaming.