
T I M E O F R A N
### Blockchain Technology ?
A Comprehensive Explanation
Introduction
Blockchain technology is a revolutionary concept that has gained significant attention in recent years. It is often associated with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, but its applications go far beyond digital currencies. In this comprehensive explanation, we will explore what blockchain technology is, how it works, its history, its various use cases, and its potential impact on industries and society as a whole. This extensive guide will cover blockchain in approximately three thousand words.
### What is Blockchain ?
Definition
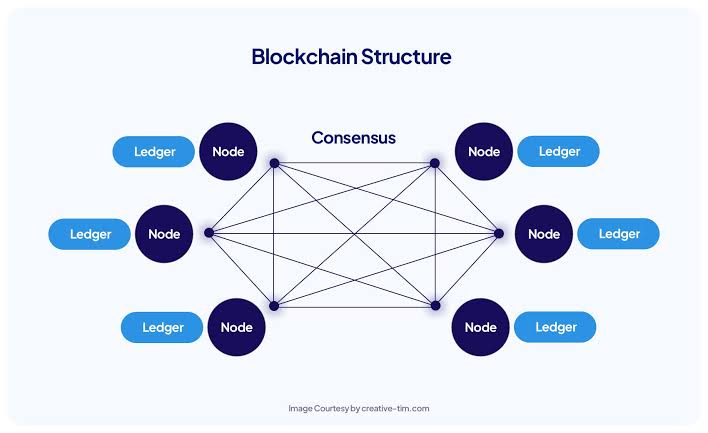
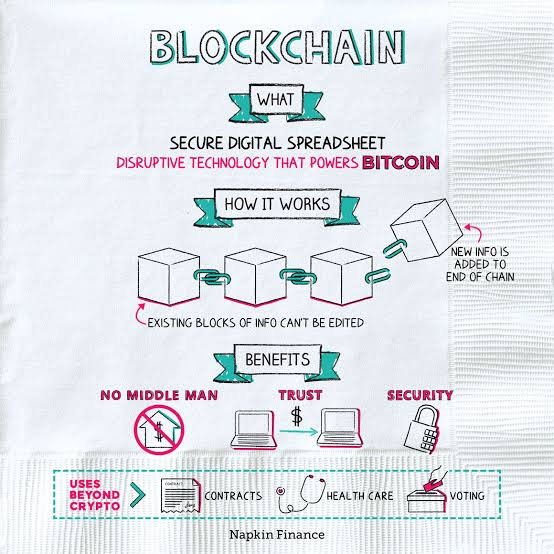
Blockchain is a decentralized and distributed ledger technology that records transactions across multiple computers. It is often referred to as a “chain of blocks” because it consists of a chain of data blocks linked together to form a secure and immutable record.
### Core Concepts ?
To understand blockchain, it’s essential to grasp some fundamental concepts:
* Decentralization : Unlike traditional centralized systems (e.g., banks), blockchain operates on a decentralized network of computers. No single entity has complete control, making it more resilient and transparent.
* Distributed Ledger : A blockchain ledger is not stored on a single computer or server but distributed across a network of nodes. Each node has a copy of the entire ledger, ensuring transparency and redundancy.
* Immutability : Once data is recorded in a blockchain, it is nearly impossible to alter or delete. This immutability is achieved through cryptographic techniques.
* Consensus Mechanisms. : Blockchains use consensus mechanisms to validate and add transactions to the ledger. The most common mechanism is Proof of Work (PoW), but there are others like Proof of Stake (PoS) and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS).
How Does Blockchain Work ?
The basic structure of a blockchain can be broken down into the following components :
* Transactions : Users initiate transactions, which involve the exchange of assets, data, or any value. These transactions are bundled into blocks.
* Blocks : A block is a collection of transactions. Each block contains a reference to the previous block, creating a chain.
* Miners/Validators : Miners (in PoW) or validators (in PoS) compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions. The first to solve it gets the right to add a new block to the chain.
* Consensus : Once a miner/validator adds a block, the network reaches a consensus on the validity of the transactions. This ensures that only legitimate transactions are recorded.
* Security : Cryptography plays a pivotal role in securing the blockchain. Transactions are cryptographically signed, and the integrity of the entire chain is maintained through hashing algorithms.
A Brief History of Blockchain ?

* Pre-Bitcoin Era
The concept of a decentralized ledger predates Bitcoin. In the early 1990s, cryptographers like Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta developed a system for timestamping documents to prevent backdating or tampering. However, their work did not gain widespread adoption.
* The Birth of Bitcoin
The true birth of blockchain technology is often attributed to the mysterious figure known as Satoshi Nakamoto. In 2008, Nakamoto published a whitepaper titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System.” This paper outlined the first practical application of blockchain as the underlying technology for a digital currency.
* The Rise of Bitcoin
In January 2009, Nakamoto mined the first Bitcoin block, known as the “genesis block.” This marked the beginning of the Bitcoin blockchain. Bitcoin rapidly gained popularity as a digital currency and a store of value, leading to a surge in its price and widespread recognition.
* Emergence of Altcoins
Bitcoin’s success paved the way for the creation of alternative cryptocurrencies or “altcoins.” These projects introduced variations in blockchain technology, such as faster transaction processing, enhanced privacy features, and different consensus mechanisms.
* Beyond Cryptocurrencies
While blockchain was initially associated with cryptocurrencies, developers soon recognized its potential for various applications beyond digital money. This led to the exploration of blockchain’s utility in fields like finance, supply chain management, healthcare, and more.
Key features of Block Chain ?
Transparency and Trust
One of the most significant advantages of blockchain is its transparency. All participants in the network have access to the same ledger, reducing the need for trust in intermediaries. This transparency enhances accountability and reduces fraud.
* * * Security and Immutability
Blockchain’s security is achieved through cryptographic techniques, making it extremely resistant to tampering or fraud. Once a transaction is added to the blockchain, it is virtually impossible to alter, ensuring the integrity of the data.
* * * Decentralization
The decentralized nature of blockchain eliminates the need for a central authority or intermediary. This reduces the risk of a single point of failure and enhances network resilience.
* * * Efficiency and Reduced Costs
Blockchain can streamline processes by removing intermediaries and automating tasks. This leads to cost savings and faster transaction settlement times.
* * * Interoperability
Many blockchain projects are working on solutions for better interoperability, enabling different blockchains to communicate and share data seamlessly. This will be crucial for the development of a blockchain-based ecosystem.
Use Cases of Blockchain ?


# Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies are the most well-known application of blockchain technology. Bitcoin, Ethereum, and thousands of other cryptocurrencies use blockchain to enable secure, peer-to-peer digital transactions.
# Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement written directly into code. They automate contract execution and eliminate the need for intermediaries. Ethereum is a popular blockchain for creating and executing smart contracts.
# Supply Chain Management
Blockchain can enhance transparency and traceability in supply chains. It allows consumers and businesses to track the journey of products, ensuring authenticity and quality.
# Healthcare
Blockchain can securely store and share medical records, ensuring patient data privacy and enabling faster and more accurate diagnoses and treatments.
# Voting Systems
Blockchain has the potential to revolutionize voting systems by providing secure and transparent voting processes, reducing the risk of fraud and manipulation.
# Finance
Blockchain technology is transforming the financial industry. It enables faster, more cost-effective cross-border payments, reduces fraud, and opens up new opportunities in lending, insurance, and asset tokenization.
# Intellectual Property
Blockchain can be used to prove ownership of intellectual property, such as patents, copyrights, and trademarks, making it easier to protect and license creative works.
# Identity Verification
Blockchain offers a secure and decentralized solution for identity verification, reducing the risk of identity theft and simplifying the process of proving one’s identity.
# Real Estate
The real estate industry can benefit from blockchain’s ability to streamline property transactions, reduce fraud, and improve transparency in property records.
# Energy Trading
Blockchain allows for peer-to-peer energy trading, enabling consumers to buy and sell excess energy directly to one another, reducing dependence on centralized energy providers.
Challenges and Limitations of Blockchain ?
# Scalability
As the number of transactions on a blockchain grows, scalability becomes a significant challenge. Some blockchains struggle to process transactions quickly and cost-effectively.
# Energy Consumption
Proof of Work blockchains, like Bitcoin, require significant computational power, leading to high energy consumption. This has raised concerns about the environmental impact of

Thank You ❤️
Write :- By… [ -: TIME OF RAN :- ]